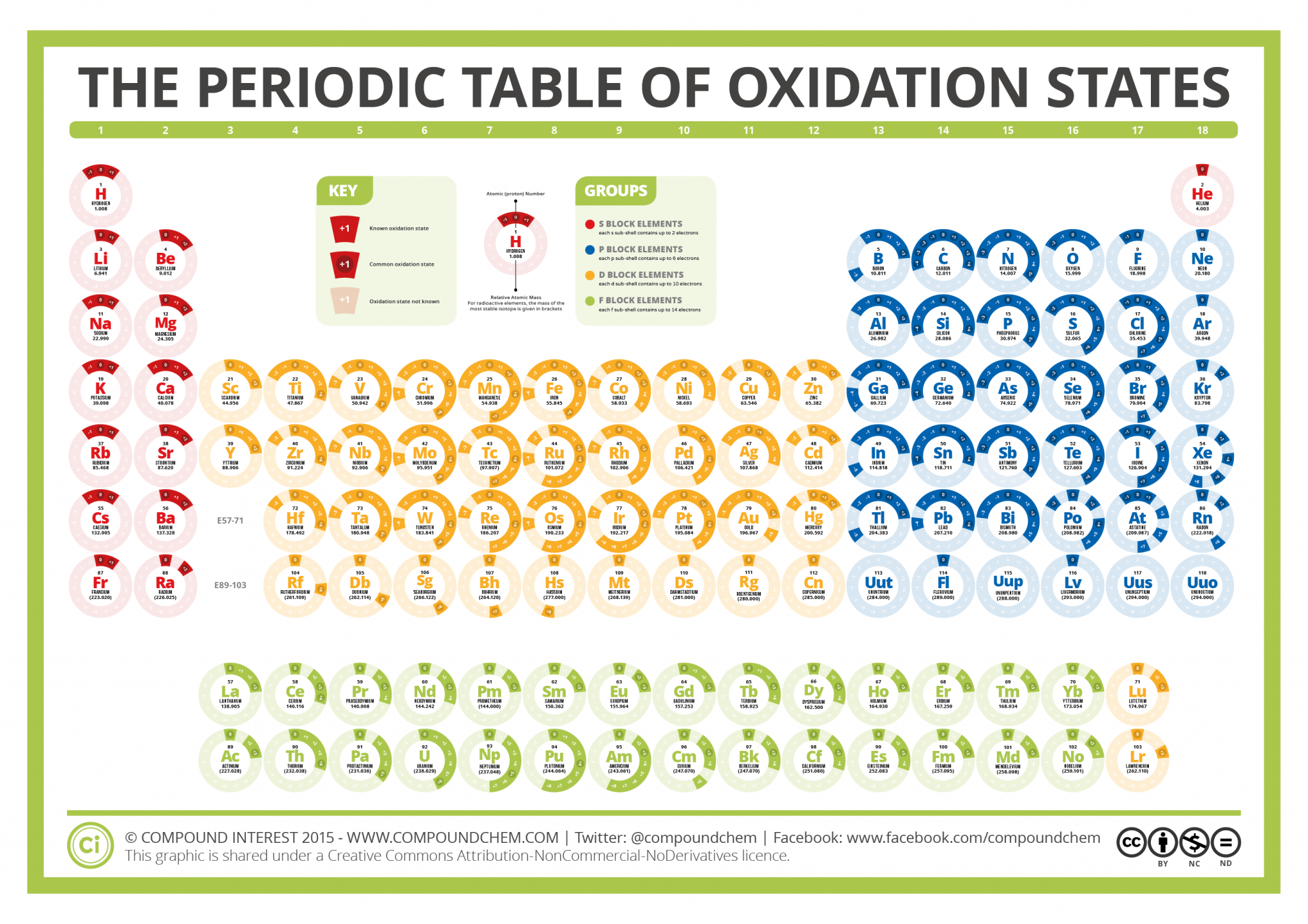
Compound Interest The Periodic Table of Oxidation States
Enter the formula of a chemical compound to find the oxidation number of each element. A net ionic charge can be specified at the end of the compound between { and }. For example: ZnCl4{2-} or NH2NH3{+}. Enter just an element symbol to show the common and uncommon oxidation states of the element.

Oxidation Number (State) Definition, Rules, How to Find, and Examples
These have oxidation numbers of +2 & +3 respectively. With a chlorine ion (a chlorine atom that has gained one electron, Cl -), the oxidation number would be -1. Oxidation state 0 occurs for all elements - it is simply the element in its elemental form. As the table shows, the presence of the other oxidation states varies, but follows.
The Nameinator Finding Oxidation Numbers
This number is defined as the formal charge on the atom if all bonds were assumed to be fully ionic. Knowing the oxidation state is very useful for example when balancing reduction-oxidation (redox) reactions. Figure 1: Oxidation states in the Periodic Table. Referred from: Article. Oxidation numbers for atoms, ions and compounds.

The Periodic Table of Oxidation States Compound Interest
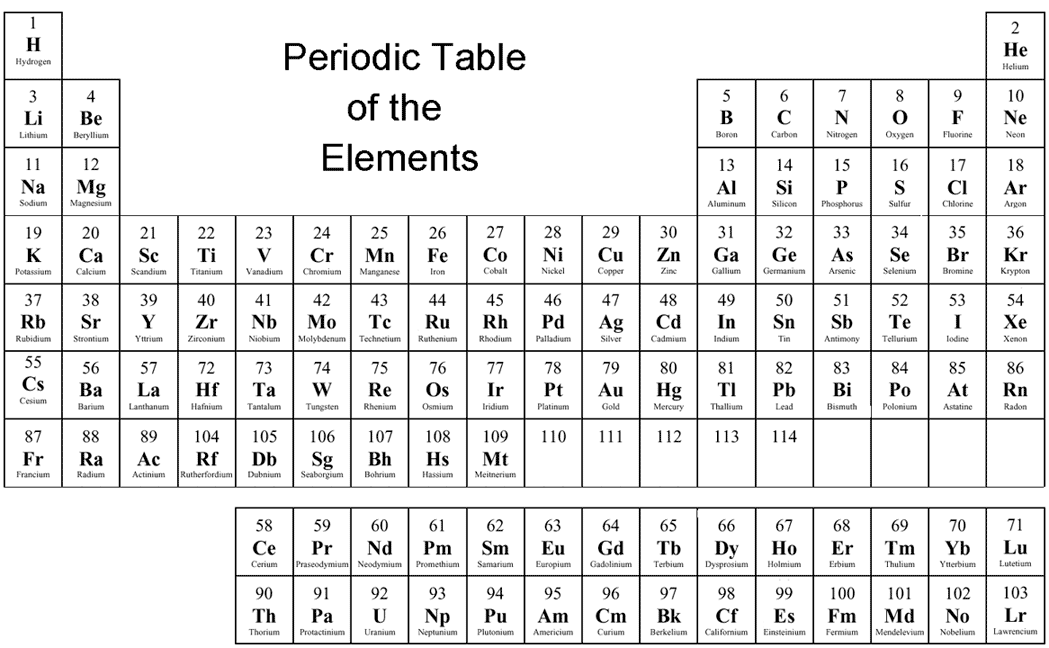
Interactive periodic table showing names, electrons, and oxidation states. Visualize trends, 3D orbitals, isotopes, and mix compounds.. 3D orbitals, isotopes, and mix compounds. Fully descriptive writeups. Periodic Table of Elements. Properties Electrons Isotopes Compounds. or buying a poster or wallet card, order number. 1H Hydrogen 1..
Oxidation Numbers Periodic Table Elements
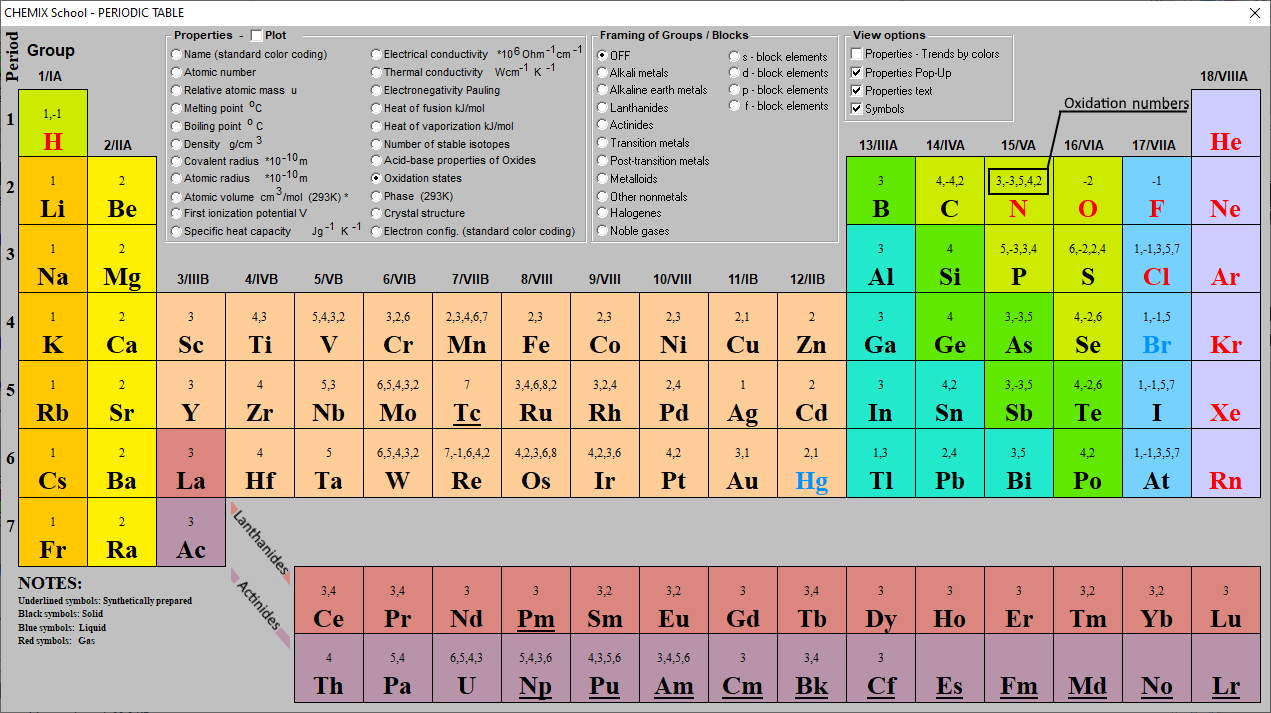
This. Oxidation States table gives the Oxidation States of all the elements of periodic table. Click on 'Element Atomic Number', 'Element Symbol', 'Element Name' and 'Element Oxidation States' headers to sort.

Nomenclature
EDIT: This table has been updated to include corrections in the atomic masses of iron and gallium. The corrected table can be found here. This printable periodic table contains the number, symbol, name, atomic mass and oxidation states of each element. The most common oxidation states are in bold text and predicted or unconfirmed states are in.

The Periodic Table of Oxidation States Oxidation state, Teaching
9. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is zero. H 2 O: 2(+1) + (-2) = 0. 10. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge on the ion. The oxidation number of the sulfur atom in the SO 4 2-ion must be +6, for example, because the sum of the oxidation numbers of the atoms in this ion must equal -2.
Oxidation Numbers
The oxidation number of any free element is 0. The atoms in Na, O 2, N 2, Pb, He, H 2, Ne, Zn, for example, have oxidation numbers of 0.. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to the charge on the ion. For example, the oxidation number of chlorine in the Cl-ion is -1. The oxidation number of bromine in the Br-ion is -1. The oxidation number of sodium in the Na + ion is +1.

Downloadable Periodic Table Oxidation States
This periodic table contains the atomic number, element symbol, element name, atomic weights and oxidation numbers. Todd Helmenstine. This periodic table contains the oxidation numbers of the elements. Bold numbers represent the more common oxidation states. Values in italics represent theoretical or unconfirmed oxidation numbers. This table.
Aluminum Aluminum Oxidation Number
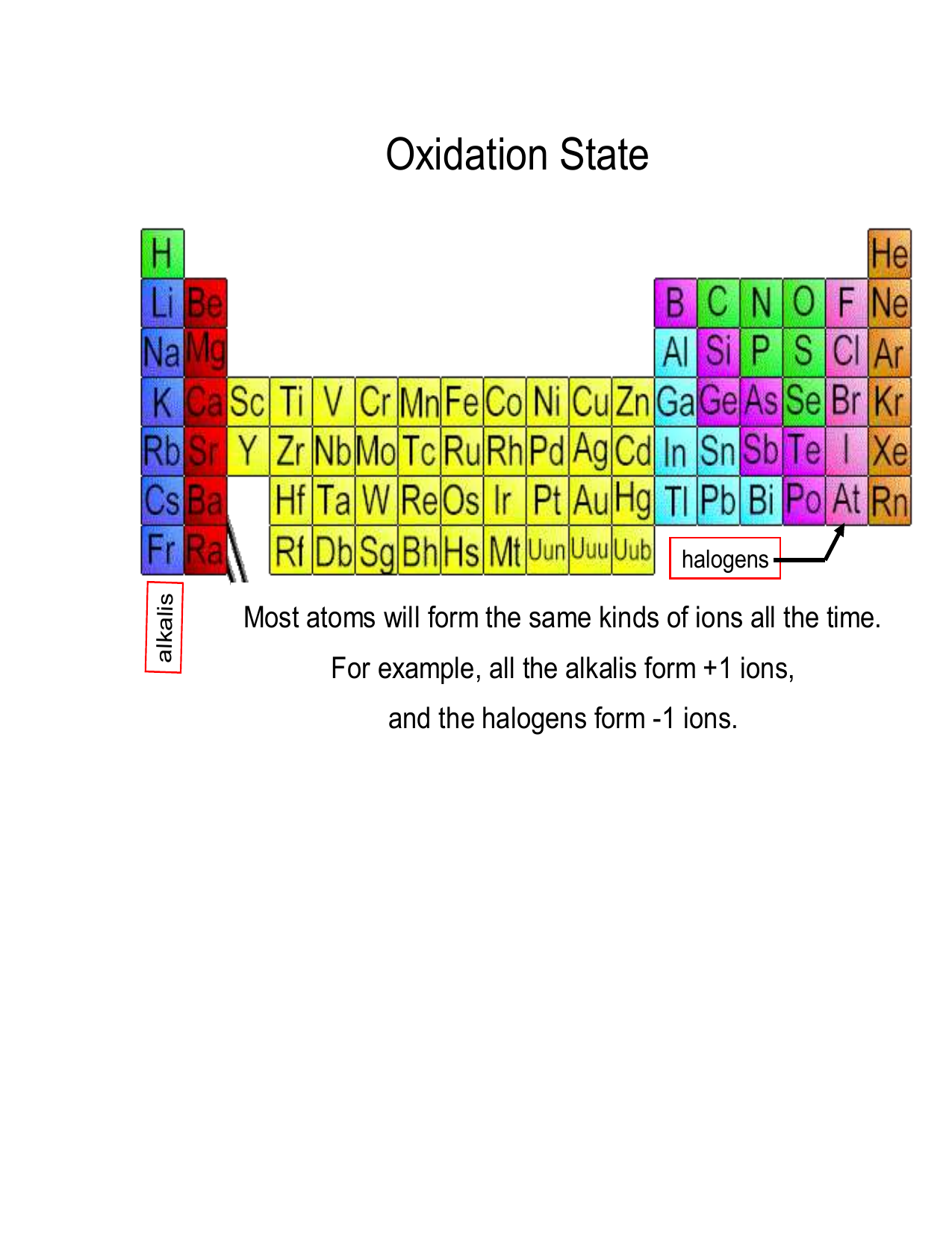
The oxidation number of a monatomic ion (by itself or as part of an ionic compound) is equal to its charge. Alkali metals - elements in the first column of the periodic table - will always have an oxidation number of +1; Alkali metals (column 2) are almost always +2

The Periodic Table of Oxidation States Compound Interest
Oxidation numbers are used to track how many electrons are lost or gained in a chemical reactions. Assigning these numbers involves several rules: Free atoms (H2) usually have an oxidation number of 0, monoatomic ions (Cl-) are usually equal to their charge, and polyatomic ions have several governing principles.
Printable Periodic Table With Oxidation Numbers Printable Word Searches
Oxidation numbers; Monoatomic ions oxidation numbers; Polyatomic ions oxidation numbers; Periodic table with oxidation numbers; Steps to writing chemical formulas; Molecular and Empirical Formulas; Molecular mass and formula mass; Types of chemical compounds; Binary compounds; Ternary compounds
/PeriodicTableOxidation-BW-56a12da83df78cf772682bfe.png)
Periodic Table With Groups Numbers Periodic Table Timeline
The positive oxidation state is the total number of electrons removed from the elemental state. It is possible to remove a fifth electron to form another the \(\ce{VO_2^{+}}\) ion with the vanadium in a +5 oxidation state.. Remember that electronegativity is greatest at the top-right of the periodic table and decreases toward the bottom-left.
/PeriodicTableOxidation-BW-56a12da83df78cf772682bfe.png)
Periodic Table of the Elements Oxidation Numbers
Periodic Table With Element Valences. This information is available on a Color Periodic Table of the Elements or a Black and White version. A simpler version listing only the most common oxidation state charges is also available. References. Brown, I. David (2016). Inorganic Chemistry: The Bond Valence Model (2nd ed.). International Union of.
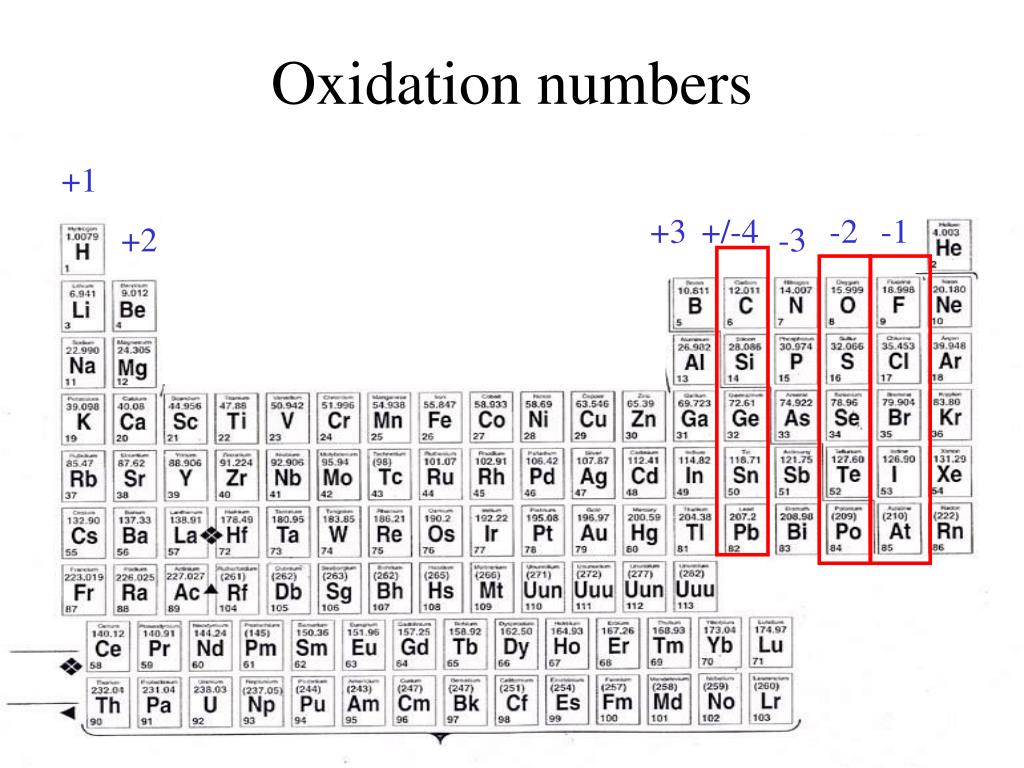
PPT Elements and Periodic Table PowerPoint Presentation, free
EDIT: This table has been updated to include corrections in the atomic masses of iron and gallium. The corrected table can be found here. This color periodic table contains the number, symbol, name, atomic mass and oxidation states of each element. The most common oxidation states are in bold text and predicted or unconfirmed states are in italics.
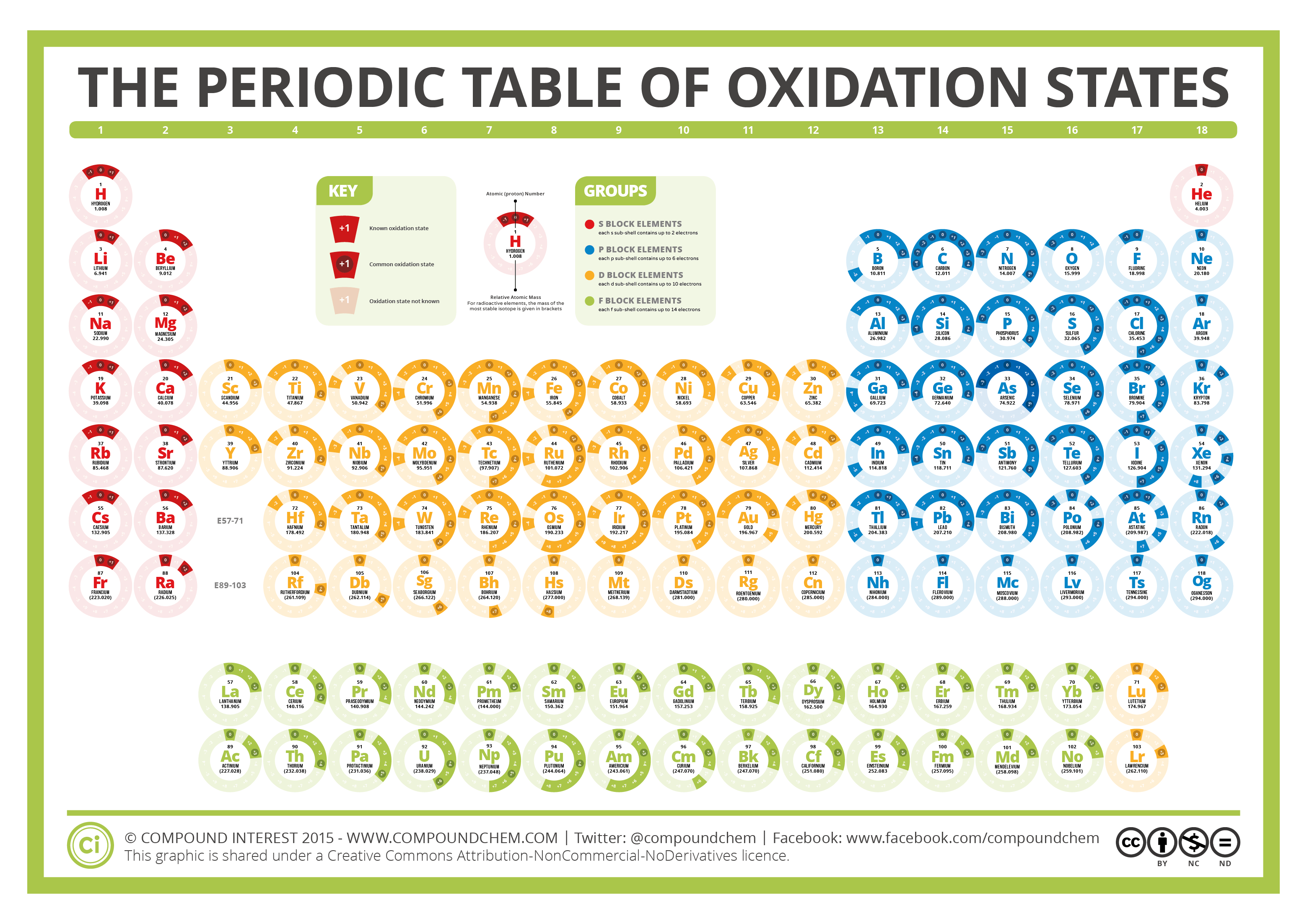
The Periodic Table of Oxidation States Compound Interest
Oxidation number of an atom when an element has combined with the same element. When an element has combined with same kind element, it's oxidation number becomes 0. Ex: oxidation number of Bromine in Br 2 molecule is 0. Table: oxidation numbers of first 20 elements in the periodic table according to the atomic number